On first connection the display of the head unit should be active.
If this is not the case check the fuse in the +B1 cable and also check the cable itself and its terminals.
In case the temperature sensor is used:
The temperature sensor M8 cable lug must be connected to the positive pole of the battery bank (the red wire of the sensor doubles as the power supply wire).
Check the fuse in the positive (red) cable.
Make sure the correct temperature sensor is used. Note that the MultiPlus temperature sensor is not suitable.
Make sure the temperature sensor has been connected the right way. The red cable should connect the +B1 terminal and the black wire to the +B2 terminal.
See the Auxiliary connection for temperature monitoring chapter for connection instructions and a wiring diagram.
Check the fuse in the +B2 cable and also check the cable itself and its terminals.
In case a second battery (starter battery) is monitored:
Make sure the second battery negative is connected to the load side of the battery monitor shunt. See the chapter Auxiliary connection for monitoring the voltage of a second battery for connection instructions and a wiring diagram.
In case the temperature sensor is used:
The temperature sensor M8 cable lug must be connected to the positive pole of the battery bank (the red wire of the sensor doubles as the power supply wire).
Check the fuse in the positive (red) cable.
Make sure the correct temperature sensor is used. The MultiPlus temperature sensor does not work with the battery monitor.
Make sure the temperature sensor has been connected the right way. The red cable should connect to the +B1 terminal and the black wire to the Aux+B2 terminal.
See the Auxiliary connection for temperature monitoring chapter for connection instructions and a wiring diagram.
Settings can only be changed if the battery monitor is running on the most up to date firmware. Update to the latest firmware with the VictronConnect app.
It is highly unlikely that the Bluetooth interface is faulty. Some pointers to try before seeking support:
Is the battery monitor connected to a VE.Direct Bluetooth Smart dongle? The battery monitor does not have built-in Bluetooth. The VE.Direct Bluetooth Smart dongle needs to be connected to the VE.Direct terminal of the head unit to equip the battery monitor with Bluetooth.
Is the battery monitor powered up? The display on the head unit should be active. If not see the Unit is dead chapter.
Is another phone or tablet already connected to the battery monitor? Only one phone or tablet can be connected to the battery monitor at any given time. Make sure no other devices are connected and try again.
Is the VictronConnect app up to date?
Are you close enough to the battery monitor? In an open space, the maximum distance is about 20 meters.
Are you using the Windows version of the VictronConnect app? This version is unable to connect via Bluetooth. Use Android, iOS or macOS instead (or use the USB - VE.Direct interface).
Has Bluetooth been turned off in the settings? See the ??? chapter.
For connection issues, see the troubleshooting section of the VictronConnect manual: https://www.victronenergy.com/live/victronconnect:start.
Note that the PIN code is only applicable when connecting to the battery monitor via Bluetooth.
If you have lost the PIN code you will need to reset the PIN code to its default PIN code, see the Reset PIN code chapter.
More information and specific instructions can be found in the VictronConnect manual: https://www.victronenergy.com/live/victronconnect:start.
The charge current should be shown as a positive value. For example: 1.45A.
The discharge current should be shown as a negative value. For example: -1.45A.
If the charge and discharge currents are reversed, the negative power cables on the battery monitor must be swapped.
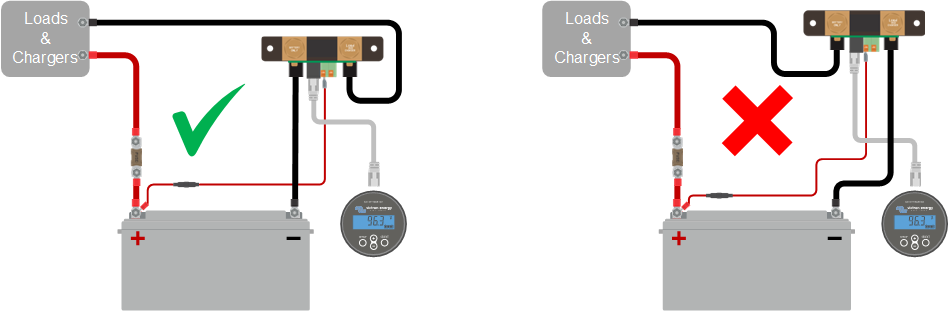 |
The negatives of all the loads and the charge sources in the system must be connected to the system minus side of the shunt.
If the negative of a load or a charge source is connected directly to the negative battery terminal or the “battery minus” side on the shunt, their current will not flow through the battery monitor and will be excluded from the overall current reading and the state of charge reading.
The battery monitor will display a higher state of charge than the actual state of charge of the battery.
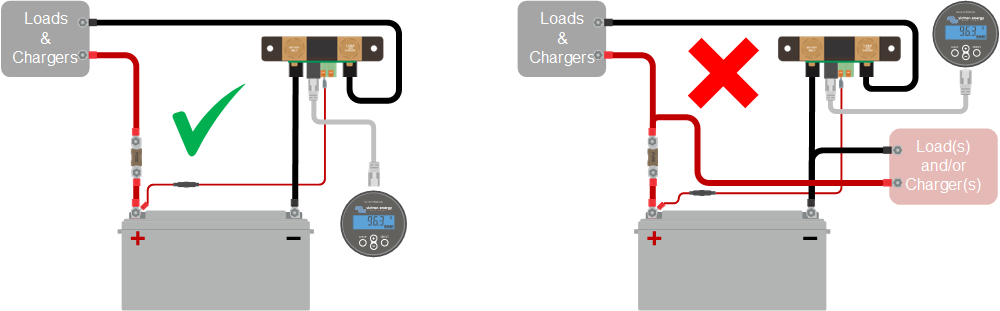 |
If there is a current reading while no current is flowing through the battery monitor, perform a zero current calibration while all loads are turned off or set the current threshold.
An incorrect state of charge can be caused by a variety of reasons.
Incorrect battery settings
The following parameter(s) will have an effect on the state of charge calculations if they have been set up incorrectly:
Battery capacity.
Peukert exponent.
Charge efficiency factor.
Incorrect state of charge due to a synchronisation issue:
The state of charge is a calculated value and will need to be reset (synchronised) every now and then.
The synchronisation process is automatic and is performed each time the battery is fully charged. The battery monitor determines that the battery is fully charged when all 3 "charged" conditions have been met. The "charged" conditions are:
Charged voltage (Voltage).
Tail current (% of battery capacity).
Charge detection time (minutes).
A practical example of the conditions that need to be met before a synchronisation will take place:
The battery voltage has to be above 13.8V.
The charge current has to be less than 0.04 x battery capacity (Ah). For a 200Ah battery, this is 0.04 x 200 = 8A.
Both above conditions have to be stable for 3 minutes.
If the battery is not fully charged or if the automatic synchronisation does not happen, the state of charge value will start to drift and will eventually not represent the actual state of charge of the battery.
The following parameter(s) will have an effect on automatic synchronisation if they have been set incorrectly:
Charged voltage.
Tail current.
Charged detection time.
Not occasionally fully charging the battery.
For more information on these parameters see the chapter: "Battery settings".
Incorrect state of charge due to incorrect current reading:
The state of charge is calculated by looking at how much current flows in and out of the battery. If the current reading is incorrect, the state of charge will also be incorrect. See paragraph Incomplete current reading.
This means that the battery monitor is in an unsynchronised state. This can occur when the battery monitor has just been installed or after it has been unpowered for some time and is being powered up again.
To fix this, fully charge the battery. Once the battery is close to a full charge, the battery monitor should synchronise automatically. If that doesn't work, review the synchronisation settings.
If you know the battery is fully charged but don't want to wait until the battery synchronises, then perform a manual synchronisation, see paragraph Synchronise SoC to 100%.
The battery monitor will automatically synchronise and reset the state of charge to 100% as soon as the battery has been fully charged. In case the battery monitor does not reach a 100% sate of charge, do the following:
Fully charge the battery and check if the battery monitor correctly detects if the battery is fully charged.
If the battery monitor does not detect that the battery has been fully charged you will need to check or adjust the charged voltage, tail current and/or charged time settings. For more information see Automatic synchronisation.
One reason could be that the negative cables going in and out of the battery monitor have been wired the wrong way around, see Charge and discharge current are inverted.
This can happen when the battery monitor thinks the battery is bigger or smaller than in reality. Check if the battery capacity has been set correctly.
Check if there is an issue with the +B1 cable. Perhaps the fuse, the cable itself or one of the terminals is faulty or there is a loose connection.
Check for incorrect wiring: the +B1 cable has to be connected to the positive of the battery bank, not midway of the battery bank.
In case a temperature sensor is used, make sure the sensor is connected to the positive terminal of the battery bank, not in the middle of the battery bank.
If the auxillary (starter) battery voltage is too low:
Perhaps there is an issue with the +B2 cable, perhaps the fuse, the cable itself or one of the terminals is faulty, or there is a loose connection.
If the auxillary (starter) battery voltage reading is missing:
Make sure that both batteries share a common negative and that the starter battery negative is connected to the load side of the battery monitor shunt. For instructions on how to correctly wire the starter battery, see Aux connection for monitoring the voltage of a second battery.
If the battery monitor does not synchronise automatically, one possibility could be that the battery never reaches a fully charged state. Fully charge the battery and see if the state of charge eventually indicates 100%.
Another possibility is that the charged voltage setting should be lowered and/or the tail current setting should be increased.
It is also possible that the battery monitor synchronises too early. This can happen in solar systems or in systems that have fluctuating charge currents. If this is the case change the following settings:
Increase the “charged voltage" to slightly below the absorption charge voltage. For example: 14.2V in case of 14.4V absorption voltage (for a 12V battery).
Increase the “charged detection time” and/or decrease the "tail current" to prevent an early reset due to passing clouds.