Take care when unpacking the battery. Batteries are heavy. Do not lift the battery by its terminals or by its BMS cables. The battery has two carry handles on either side. The weight of the battery can be found in the Technical data chapter.
Familiarise yourself with the battery. The main battery terminals on the top have a “+” symbol for positive and a “-” symbol for negative to ensure correct polarity.
Each battery has two BMS cables for communicating with the BMS. One cable has a male 3-pole connector, and the other has a female 3-pole connector. Depending on the battery model, the BMS cables are located on one side of the battery or two opposite sides of the battery.
Ensure that the BMS cables do not get snagged or damaged when handling the battery.
Top view and side views showing battery terminals (+ and -), BMS cables, and carry handles
Download the VictronConnect app for Android, iOS or macOS from their respective app stores. For more information about the app, see the VictronConnect product page.
The VictronConnect app communicates with the BMS via Bluetooth
When the BMS firmware is updated, the battery firmware is also automatically updated. This happens either via the VictronConnect app or, in the case of a Lynx Smart BMS NG in conjunction with a GX device, via the VRM portal. Also, make sure you have the latest VictronConnect version. This ensures that the latest battery and BMS firmware version is available.
The VictronConnect app might ask to update the firmware on the first connection. If this is the case, let it perform a firmware update.
If one or more batteries are added to the system at a later date, the battery firmware will be automatically updated by the BMS.
To check the battery and BMS firmware version, do the following:
This section only applies if you intend to connect batteries in series.
Lithium batteries are only approximately 50 % charged when shipped from the factory. This is a transportation safety requirement. However, due to differences in transportation routes and warehousing, the batteries do not always have the same state of charge by the time they are installed.
Individually charging new batteries before connecting them in series will shorten the charging time.
The built-in battery cell balancing system can only correct small differences in state of charge from one battery to another. New batteries can have large state of charge differences between them that won't be corrected if installed that way, especially when connected in series. Please note that differences in state of charge between batteries is not the same thing as imbalances between cell voltages within a battery. This is because the cell balancing circuits in one battery cannot affect the cells in another battery.
Warning
Always use a BMS-controlled charger when individually charging lithium batteries.
Initial charge procedure:
If a battery bank consists of batteries connected in series to make a higher voltage bank, each battery must first be charged individually. Use a dedicated charger or an inverter/charger with a BMS to perform the initial charge.
Only a single battery or a bank of parallel connected batteries can be charged as one.
Refer to the BMS manual for instructions on how to set it up.
Set the charger to the charge profile as indicated in the Charging the battery and recommended charger settings section.
Ensure that the battery, the BMS and the charger are communicating with each other. Check this by disconnecting one of the battery BMS cables from the BMS and verifying that the charger turns off. Then reconnect the BMS cable and verify that the charger turns back on.
Turn the charger on and check that the charger is charging the battery.
Note that if, during charging, there is any imbalance between the battery cells, then the BMS may turn the charger off and on repeatedly. You may notice that the charger is turned off for a few minutes and then on again for a short period of time before being turned off again. Don't be alarmed; this pattern will repeat itself until the cells are balanced. If the cells are balanced, then the charger will not turn off until the battery is fully charged.
The battery is fully charged when the battery charger has reached the float stage and the VictronConnect app battery cell status is "balanced." If the battery cell status is "unknown" or "imbalanced," the battery charger will be restarted multiple times until it is "balanced".
Initial charge using a BMS
Mounting must meet the following requirements:
The battery can be mounted upright or on its side, but not with the battery terminals facing down.
The battery is only suitable for indoor use and needs to be installed in a dry location.
Batteries are heavy. When moving the battery into its destined location, use suitable handling equipment for transportation.
Ensure adequate and secure mounting, as the battery can become a projectile if involved in a vehicle accident.
Batteries produce a certain amount of heat when they are charged or discharged. Keep a 20 mm space on all four sides of the battery for ventilation.
Observe the battery polarity when connecting the battery terminals to a DC system or other batteries. Take care not to short-circuit the battery terminals.
Connect the cables as indicated in the diagram:
| 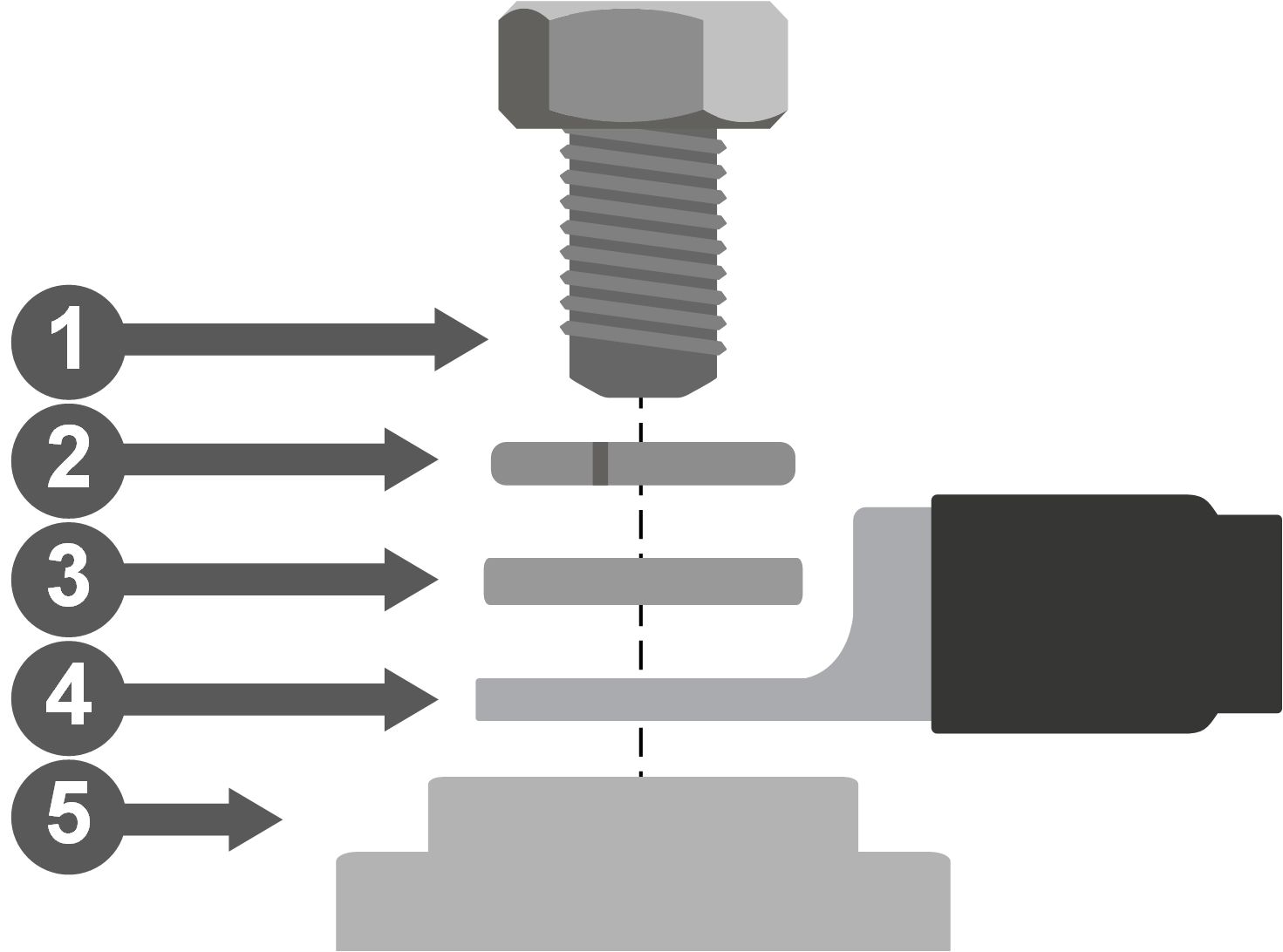 Battery cable connection | Battery terminals |
Important
Tighten the bolts with a torque of 10 Nm. Only use insulated tools that match the bolt head size.
Use battery cables with a cross-sectional area that matches the currents that can be expected in the battery system.
Batteries can produce very large currents; it is essential that all electrical connections to the battery are fused.
The battery cables must be sized to carry the maximum expected system current, and an appropriately rated fuse for the battery cable size must be used.
For more information on cable cross-sectional area, fuse types and fuse ratings, please see the Wiring Unlimited book.
The battery maximum discharge rating is indicated in the Technical data table. The system current and therefore the fuse rating should not exceed this current rating. The fuse has to match the lowest current rating, that being the cable current rating, the battery current rating or the system current rating.
| Single battery |
| Multiple batteries in series |
| Multiple batteries in parallel |
| Multiple batteries in series/parallel Do not interconnect midpoints nor connect anything else at the midpoints |
When constructing a battery bank, ideally, all batteries should be of the same capacity, age and model. However, there are situations where this is impossible, such as when capacity needs to be expanded by adding more batteries or when a single battery in a battery bank needs to be replaced. In these cases, follow the guidelines in the table below.
Battery bank type | Different capacities allowed? | Different ages allowed? |
|---|---|---|
Parallel | Yes | Yes |
Series | No1) | Yes2) |
Series/parallel - within a series string | No1) | Yes2) |
Series/parallel - in case a whole series string is replaced or added | Yes | Yes |
1) All batteries must have the same capacity rating and the same part number 2) The age difference should not exceed 3 years | ||
Background information:
Due to old batteries having reduced capacity, connecting them in series with new batteries or connecting different capacity batteries in series will result in an imbalance between the batteries. This imbalance will increase over time and cause an overall reduction in battery bank capacity. Theoretically, the battery with the lowest capacity would determine the overall capacity of a series string, but in reality, the overall series string capacity will reduce further over time. For example, if a 50Ah battery is connected in series with a 100Ah battery, the overall string capacity is 50Ah. But over time, the batteries become imbalanced, and when the imbalance has become, let's say, 10Ah, the overall battery capacity will be 50Ah-10Ah = 40Ah. The cells of the fullest battery will have an overvoltage during charging, while they are not able to send the excess voltage to the other battery cells. The BMS will constantly interfere, resulting in the emptiest battery is being discharged too deeply and the fullest battery is being overcharged.
Each battery has two BMS cables with an M8 male and M8 female connector that need to be connected to the BMS.
BMS cables on either side or on one side | Female and male BMS connector Connected BMS connectors |
How to connect the cables:
For a single battery, connect both cables directly to the BMS.
For a battery bank consisting of multiple batteries, interconnect each battery (daisy chain) and connect the first and last cable to the BMS. The batteries can be interconnected in any order.
If the BMS is too far away for the cables to reach, use the optional extension cables. The extension cables are available as a pair and come in various lengths. For more information, see the extension cable product page.
Single battery BMS connection | Two battery BMS connection (with optional extension cables) | Multiple battery BMS connection |
The recommended charging parameters for the charging sources are:
For 12.8V models: 14.2V absorption voltage, 2 hours absorption time and 13.5V float voltage
For 25.6V models: 28.4V absorption voltage, 2 hours absorption time and 27.0V float voltage
For the 51.2V model: 56.8V absorption voltage, 2 hours absorption time and 54.0V float voltage
For the recommended charge currents, please see the Charging the battery and recommended charger settings chapter and refer to the table in the Technical data chapter.
For more information on the charging settings of the individual chargers or inverters/chargers, please refer to the manuals on the respective product page.
Adjusting charging voltages is not required for DVCC-controlled inverters/chargers and chargers such as the Orion XS and MPPT solar chargers. This setting is automatic and slightly different from a manual setting. For more information about DVCC, see your GX device manual on the respective product page.
Once all connections have been made, the system wiring needs to be checked, the system needs to be powered up, and the BMS functionality needs to be checked. Follow this checklist:
Check the polarity of all battery cables. | |
Check the cross-sectional area of all battery cables. | |
Check if all battery cable lugs have been crimped correctly. | |
Check if all battery cable connections are tight (don’t exceed maximum torque). | |
Tug slightly on each battery cable and see if the connections are tight. | |
Check all BMS cable connections and make sure the connector screw rings are screwed all the way down. | |
Connect the system positive and negative DC cable to the battery (or battery bank). | |
Check the string fuse(s) rating (if applicable). | |
Install the string fuse(s) (if applicable). | |
Check the main fuse rating. | |
Install the main fuse. | |
Check if all battery charge sources have been set to the correct charge settings. | |
Turn on all battery chargers and all loads. | |
Check if the BMS is powered up. | |
Disconnect a random BMS cable and verify that the BMS is turning off all charge sources and all loads. | |
Reconnect the BMS cable and check if all charge sources and loads turn back on. |
